Different examples of the use of IoT in agriculture are found in daily life. IoT has a significant role in almost every field of life, including the health, construction, engineering, industrial, home, automotive, and agriculture sectors. It is a revolutionary period from the last decade. IoT prevails almost all over human life and has significant impacts worldwide.
What is IoT?
IoT stands for the Internet of Things. The Internet of Things means the smart gadgets or devices used for various task management. Examples are health-related gadgets, auto cars, GPS, and other climate-related gadgets.
IoT gadgets or devices help a lot in managing various agriculture-related projects, home automation, etc. The security camera is also an IoT gadget that surveils your home from bugs.
How IoT Impacts Agriculture
Smart farming is already making a massive difference in the industry with its ability to optimize resources, reduce waste and increase agricultural productivity.
IoT in agriculture refers to using smart devices and sensors to monitor agricultural processes, from planting to tillage to harvest and final distribution.
Using IoT sensors, farmers can collect environmental data (such as rainfall, humidity, pollution, etc.) to make data-driven decisions that improve every aspect of the farming process.
One example is sensors that monitor soil conditions, allowing farmers to determine the amount of pesticides and fertilizers they need to inject into the soil for optimal growth efficiency.
Global Agricultural IoT Market Size
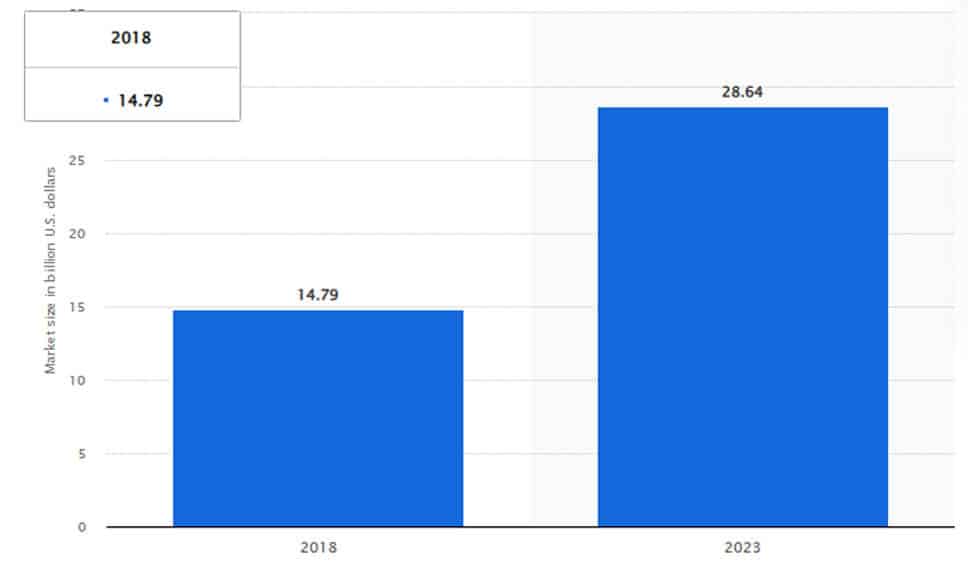
According to a well-known organization Statista, the global market of the use of IoT in agriculture from 2018 and 2023 is surprising. In 2018 it was 14.79 billion U.S. dollars, which will increase by 28.64 billion Us dollars in 2023.
Figures are shocking, and IoT applications will go up every year in the future because, now, traditional agriculture is replaced with the IoT for better growth to meet the world’s need for overpopulation.
Traditional farming will be replaced with intelligent agriculture in the last few years. IoT technology has increased efficiency and accuracy in plantation, growing, harvesting, and collecting the data of crops. Accordingly, the strategy can be changed for the better growth of the crop.
In 2020, IoT precision crop farming was 7.28 billion U.S. dollars, expected to increase to more than 13 billion U.S. dollars in 2026.
IoT Wireless & Cellular Devices Installed In Agriculture Worldwide
According to Statista organization, 0.8 million IoT cellular connections were installed in agriculture globally in 2016 and 3.1 million in 2021. Similarly, 17 million IoT wireless devices have been installed in agriculture globally in 2016, and increased by 27.4 million in 2021.
Over time, it will increase day by day, and the reason is better to grow more and more crops to meet the need of the population of the world.
Applications of IoT in Agriculture (Examples)
No one can deny the benefits of IoT in agriculture and other fields of life, including health and fitness, home automation, gardening, automobiles, etc. Artificial Intelligence plays a crucial role in IoT things or devices to get the requisite results.
1. Soil preparation management
Click the image to buy on Amazon.
IoT soil monitoring uses technology to enable farmers and growers to maximize yields, reduce disease and optimize resources. IoT sensors can measure soil temperature, NPK, volumetric water content, photosynthetic irradiance, soil water potential, and soil oxygen content.
The IoT sensor data is then sent to a central point (or cloud) for analysis, visualization, and trending. The data generated can be used to optimize agricultural processes, identify trends and optimize conditions to maximize yield and quality.
The following factors are measured during soil preparation.
- Moisture
- Temperature
- Radiation
- nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK)
- Vapor pressure
- Soil oxygen level
2. Weather data monitoring
Traditionally, farms have relied on weather forecasts from the nearest airport or city, which did not provide sufficiently accurate readings. With hyper-local weather sensors based on Edge IoT technology, farms can avoid weather surprises and plan accordingly.
With detailed knowledge of the local climate, farmers can refine their cultivation strategies and increase their yields. The weather plays a vital role in agriculture. And the need for environmental knowledge drastically reduces agricultural production’s quantity and quality.
But, IoT solutions allow a farmer to know the weather conditions in real time. Sensors are placed on and around agricultural fields. The IoT ecosystem includes sensors that can detect weather conditions, such as humidity, precipitation, temperature, etc., very accurately and in real-time.
If extreme weather conditions are detected, an alert will be sent. The need to be physically present during unstable weather conditions is eliminated, ultimately increasing productivity and helping farmers get the most out of farming.
allMETEO, Smart Elements and Pycno are the few IoT devices to measure the weather around the area of the agricultural crop or field. These IoT work remotely and send data to the cloud for analysis and prudent decisions to the farmer.
Check Amazon For Weather Solutions
3. Crop monitoring and management
Farmers can use IoT technology to monitor their crops. Sensors in each field can monitor the soil and collect temperature, humidity, and fertility data. Weed growth, water level, and pest and animal infestation can be detected.
Development and monitoring of potential threats sensors are available. Crop monitoring uses sensors, drones, and satellites to monitor crop health and identify areas that need special attention. The systems include all data such as crop conditions, humidity, rainfall, temperature, etc.
Crop management devices are another type of IoT product in agriculture and precision agriculture. Like weather stations, they must be placed in the field to collect specific crop data, including temperature, rainfall to leaf water potential, and overall crop health.
4. Irrigation monitoring and management
Irrigation Management uses sensors to detect when and how much water each plant needs. It saves water and also reduces weeds and runoff. Irrigation sensors collect data from the field and send it to the cloud, making decisions and alerting it accordingly.
The auto irrigation system is also available. The Irrigation Sensors are intelligent agricultural devices that control sprinklers. These sensors monitor soil dryness and control sprinklers accordingly to minimize the risk of under or over-watering.
Various sensor manufacturing brands are also available in the market and online market. It is a cool gadget necessary for irrigating your crop or garden.
5. Pesticides management
Sensors detect the presence of pests and then distribute crop protection products according to crop protection requirements, which helps to reduce pesticide use. It works with intelligent irrigation management to only spray where needed.
6. Fertilizer data and solution
Fertilizer management is a very crucial step in agriculture. In the IoT world, there are sensors collecting data and, in the cloud, making decisions for the farmer. A farmer can put fertilizers accordingly.
Nitrogen Phosphorus and potassium (NPK) measuring sensors are available. Similarly, wet-measuring sensors and oxygen level-measuring IoT gadgets are also available. There are other related sensors are also present for your ease.
The sensors alert the farmer for the low levels of fertilizers, and he can add more fertilizer over there accordingly. Similarly, these sensors work on data collecting and alert the farmer for the number of fertilizers for a field or a season.
Such sensors lower the cost of applying fertilizers and other needs and minimize the environmental impact.
7. Precision Farming management
Precision farming means collecting data about the crop and then adding fertilizers, watering, or other necessary things. This work is now straightforward with IoT devices. Various sensors can collect accurate data for decision-making.
Farmers can make more informed decisions about the care of their crops based on sensors collecting data on weather conditions or soil. IoT sensors test soil moisture, crop health, and real-time location tracking.
Many precision farming techniques, such as irrigation management, livestock management, vehicle tracking, and many more, are vital in increasing productivity and efficiency. Precision farming allows you to analyze soil conditions and other related parameters to improve operational efficiency.
8. Risk management
As mentioned earlier, data collection can help farmers predict their production. This ability to forecast production volume makes for better product distribution. With the help of IoT devices, a farmer can manage all the necessities of the crops and can manage every risk.
Knowing the harvest date for a particular crop, the farmer can plan the next shipment of seeds and grain for the day. The finished product is then shipped for distribution, and the next batch is immediately ready for planting.
It reduces production risk as it can help farmers avoid production bottlenecks and resulting income disruptions.
9. Cost-related data management
A one-time cost will be incurred on the purchase of IoT devices. After that, these sensors will help you to minimize every cost while applying fertilizers, watering, other pesticides, etc. Sensors are used to monitor the usage of the input data.
For example, farmers have precise knowledge of water consumption. Scientific understanding of how much water a plant needs to grow and how much it is fed will show farmers how to reduce unnecessary watering and conserve moisture.
10. Production enhancement
Quality control is already an aspect of IoT in manufacturing, where thermal sensors and other related sensors can continuously monitor quality indicators of manufactured goods and compare them to programmed codes for instant quality control from production.
The same technology could be applied to agriculture, where sensors embedded in the growing environment could scan it and ensure consistent quality across the board. It can be done by monitoring leaf color or root strength.
11. Cattle & other livestock management
As with crop monitoring, agricultural IoT sensors can be connected to livestock to monitor their health and performance. Another use case for these tracking devices is to help farmers locate stray animals.
Livestock tracking uses sensors and RFID tags to track the location and health of livestock. Farmers, based on collected data, determine the status of their inventory.
For example, RFID finds sick animals that have to isolate from the herd to avoid the rest of the livestock. The ability for farmers to use IoT-based sensors to monitor livestock thus reduces labor costs.
12. Autonomous robotic machinery
Click the image to buy on Amazon
IoT robots can replace human power requisite for agriculture works in the fields. Different autonomous machines are available for this purpose, including:
- Self-propelled tractors,
- automatic seed drills
- and agricultural drones
It can save farmers countless hours, prevent human error, and help solve the world’s agricultural labor shortage. These machines can save resources and reduce labor while increasing productivity.
For example, Modern Agrobots are automated tractors that work on fixed routes, send notifications, start work at specific times, etc. These tractors are uncrewed, which reduces labor costs for farmers.
Bear Flag Robotics is currently one of the companies working on this technology. In addition, smart farming also uses robots to plant seeds, weeds, and water. The work carried out is very demanding and laborious.
However, robots like Eco Robotics can use computer vision and artificial intelligence to detect weeds or plant seeds. These agricultural robots work smoothly and significantly reduce crop and environmental damage.
Things To Consider Before Buying IoT For Agriculture
To achieve IoT business goals, farmers can follow IoT best practices for agriculture, including:
a). Right equipment: An IoT ecosystem is only as robust as its components: a choice of sensors, relevant devices, and databases that best suit your solution.
b). Communication Continuity: Even if all of the above conditions are met, all chain elements must be interconnected using reliable communication protocols that do not compromise continuity.
c). Analysis Data: The data collected becomes valuable only if accompanied by strict measures. Therefore, purchasing data analysis tools and IoT devices is essential to access and act on the collected data. With data, growers can predict yield and quality in advance and calculate the susceptibility of their crops to adverse weather conditions.
d). Accurate Monitoring: If you choose to let technology do the watering, planting, harvesting, or other minor tasks while you take care of more important tasks, you need to invest in the right IoT monitoring tools that provide functionality, continuity, health, and progress continuously monitor.
e). Data Security: IoT technology works with large datasets collected from all areas of your business, regardless of the industry. This puts the integrity of the network at risk through attacks and data exploitation. For example, a drone transmitting data and sensors data must invest in cybersecurity platforms that protect the integrity of your digitized business.
f). Equipment maintenance: it is a significant challenge for agricultural IoT products as sensors are typically deployed in the field and are easily damaged. That’s why you must ensure your equipment is durable and easy to maintain. Otherwise, you will have to replace the sensors more often than you would like.
g). Mobile Apps: Smart farming must be suitable for use in the field. The business owner or operations manager should be able to access information locally or remotely using a smartphone or desktop computer. In addition, each connected device must be autonomous and have sufficient radio range for communication purposes and sending data to a central server.
Conclusion
IoT-based agriculture has helped implement modern technology solutions with proven knowledge. It closed the gap between production capacity and qualitative and quantitative efficiency.
Data captured by capturing and importing information from multiple sensors for real-time use or storage in a database ensures fast action and less crop damage. With smooth, intelligent end-to-end operations and better business process execution, products are processed and delivered faster to supermarkets in less time.
Read More
- Easiest Crops To Grow For Profit
- 11 Thorn Proof Gardening Gloves
- How To Build A Small Greenhouse For Vegetables
- Top Agriculture Corporations In The World
Reference Sites:
- IoT in Agriculture: 9 Technology Use Cases for Smart Farming (and Challenges to Consider) (easternpeak.com)
- 7 IoT Smart Solutions in Agriculture Sector [2021] (ubidots.com)
- IoT in Agriculture: 5 Use Cases & 5 Best Practices Implementation in 2023 (aimultiple.com)
- 5 IoT Applications in Agriculture Industry | Smart Farming Solutions (biz4intellia.com)
- Five Use Cases For IoT And Edge Cloud Technology In Smart Farming (forbes.com)
Recent Posts
Here is reply of high-demand removable wallpapers. The wallpaper industry has changed a lot in recent times, with the launch of removable wallpaper being seen as a blessing for homeowners, renters,...
Brown is an often neglected color when considering interior design but brown decor living room ideas could make your house feel warm, sophisticated, and timeless. More adaptable than any other...


